Global Demand Driving Furniture Innovation is reshaping the industry, pushing designers and manufacturers to adapt to evolving consumer preferences and technological advancements. From sustainable materials to innovative designs, the market is experiencing a dynamic transformation. Economic factors, emerging consumer tastes, and supply chain challenges are all influencing this evolution.
This shift in the furniture landscape is evident in the growing demand for customizable, sustainable, and technologically advanced pieces. Companies are innovating across all aspects of production, from design and materials to logistics and supply chains, in response to these trends.
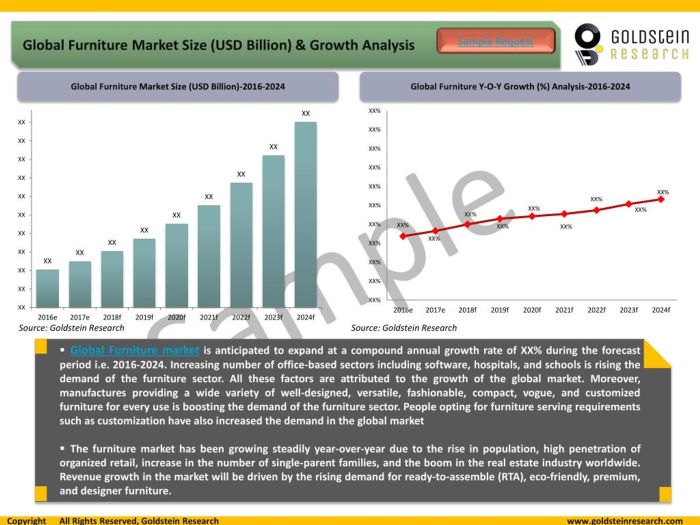
Global Market Trends
The global furniture market is a dynamic and multifaceted sector, reflecting shifting consumer preferences, economic conditions, and technological advancements. Understanding these trends is crucial for businesses to adapt and thrive in this competitive landscape. This analysis explores key aspects of the global furniture market, from current trends to future opportunities.The furniture industry is not immune to the influence of global economic forces.
Fluctuations in raw material costs, currency exchange rates, and consumer confidence levels all play a significant role in shaping demand and pricing strategies. This analysis delves into the economic factors driving demand and examines how these factors impact different regions.
Current Global Furniture Market Trends
The furniture market is evolving rapidly, with consumers increasingly seeking furniture that is both aesthetically pleasing and functionally adaptable. Sustainability is a key consideration, leading to greater interest in eco-friendly materials and production processes. Modern design aesthetics, characterized by clean lines and minimalist forms, remain popular, while also seeing a resurgence of vintage and handcrafted pieces.
Key Economic Factors Influencing Global Furniture Demand
Economic growth and stability are fundamental drivers of furniture demand. Periods of prosperity often see increased spending on home furnishings, whereas recessions can lead to a reduction in purchases. Factors like inflation, interest rates, and consumer confidence significantly impact purchasing decisions. For example, rising interest rates can make borrowing more expensive, potentially reducing demand for large-ticket items like furniture.
Emerging Consumer Preferences in Furniture Design and Function
Consumers are increasingly seeking furniture that combines functionality with aesthetic appeal. Multi-functional pieces, such as sofas with storage or tables that convert into desks, are highly sought after. Additionally, customizable furniture options allow consumers to tailor their designs to their specific needs and preferences. This trend is particularly notable in urban areas, where space optimization is paramount.
Comparison of Furniture Demand Across Regions and Cultures
Furniture demand varies significantly across different regions and cultures. In regions with strong cultural traditions, traditional furniture styles often hold significant value and continue to be in demand. Conversely, in regions with rapidly evolving lifestyles, modern and minimalist designs are gaining popularity. Cultural preferences also influence the materials used and the overall aesthetic of furniture. For example, in some Asian cultures, furniture often features intricate carvings and elaborate designs.
Significant Challenges and Opportunities in the Global Furniture Market
The global furniture market faces challenges like fluctuating raw material prices, increasing transportation costs, and the need for sustainable practices. However, opportunities abound in adapting to changing consumer preferences, embracing innovative designs, and leveraging technology to improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact. The increasing demand for customizable furniture and the growing popularity of online platforms present significant opportunities for businesses to connect with consumers directly.
Growth of the Furniture Market in Different Countries (Last 5 Years)
| Country | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States | $120 Billion | $125 Billion | $122 Billion | $130 Billion | $135 Billion |
| China | $80 Billion | $85 Billion | $90 Billion | $100 Billion | $105 Billion |
| Germany | $40 Billion | $42 Billion | $41 Billion | $45 Billion | $47 Billion |
| India | $30 Billion | $32 Billion | $35 Billion | $40 Billion | $45 Billion |
Note: Figures are approximate and represent estimated market values.
Innovation in Furniture Design
Furniture design is undergoing a period of significant transformation, driven by a confluence of factors including technological advancements, growing sustainability concerns, and evolving global lifestyles. This evolution is not just about aesthetics; it’s about functionality, durability, and environmental responsibility. Innovative designs are responding to these changing demands, offering solutions that are both beautiful and sustainable.Technological advancements are revolutionizing furniture manufacturing, leading to more efficient production methods, enhanced material properties, and the creation of entirely new design possibilities.
Simultaneously, the increasing awareness of environmental issues is prompting a shift towards sustainable materials and manufacturing processes, pushing the boundaries of creativity and ingenuity in the industry.
Impact of Technological Advancements
Advanced manufacturing techniques like 3D printing and laser cutting are enabling intricate and customized furniture designs. These technologies also allow for the creation of lighter, stronger, and more complex shapes that were previously impossible. The use of computer-aided design (CAD) software has streamlined the design process, allowing designers to visualize and test different concepts rapidly. This accelerates the prototyping phase, reducing costs and time-to-market for new products.
Furthermore, the integration of sensors and smart technologies within furniture pieces can offer personalized experiences, enhancing comfort and functionality.
Sustainability Concerns Driving Innovation
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor in furniture design decisions. Consumers are increasingly seeking furniture made from recycled or renewable materials, minimizing their environmental footprint. This is leading to innovative approaches in material sourcing and production processes. Companies are exploring bio-based materials, like bamboo and mycelium, as sustainable alternatives to traditional wood. The use of recycled plastics and other post-consumer materials is also gaining traction, showcasing a commitment to circularity in design.
Examples of Innovative Furniture Designs
Modern furniture design often incorporates modularity and adaptability. Pieces that can be rearranged or reconfigured to suit different needs and spaces are becoming increasingly popular. Ergonomic design principles are also gaining prominence, with furniture focusing on comfort and support for users. Innovative seating arrangements, for instance, are incorporating adjustable features to meet varying user preferences and postures.
Role of Design Trends and Aesthetics
Global design trends influence the demand for specific furniture styles and aesthetics. Minimalist designs, characterized by clean lines and simple forms, continue to be popular. However, there’s also a resurgence of interest in more elaborate and decorative pieces, demonstrating a diverse spectrum of design preferences. Cultural influences and artistic movements also play a significant role in shaping contemporary furniture trends.
Top 5 Innovative Furniture Materials
- Bamboo: A rapidly renewable resource with exceptional strength and durability, suitable for a wide range of furniture applications, including flooring, wall panels, and decorative accents.
- Recycled Plastics: A sustainable alternative for furniture components, from chairs to tables, reducing reliance on virgin materials and minimizing plastic waste.
- Mycelium: A naturally occurring fungal network that can be molded into furniture components. It is a biodegradable material with exceptional strength, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional materials.
- Recycled Metal: Using scrap metal to create furniture components reduces the need for new metal extraction, lowering environmental impact and offering unique aesthetic possibilities.
- Bio-based Polymers: Derived from renewable sources like corn starch or sugarcane, these polymers offer a sustainable alternative to traditional plastics, potentially for furniture components.
Comparison of Traditional and Sustainable Furniture Materials, Global Demand Driving Furniture Innovation
| Material | Traditional Furniture Material | Sustainable Alternative | Key Advantages of Sustainable Alternative |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wood | Solid hardwood (oak, mahogany) | Bamboo, reclaimed wood | Renewable resource, lower environmental impact, often stronger than traditional alternatives |
| Metal | Steel, iron | Recycled metal, aluminum | Reduces reliance on virgin materials, minimizes environmental impact of metal extraction |
| Plastics | Polystyrene, PVC | Bio-based polymers, recycled plastics | Reduced reliance on fossil fuels, reduced plastic waste |
| Fabric | Cotton, synthetic fibers | Recycled textiles, organic cotton | Sustainable sourcing, reduced environmental impact from textile production |
Supply Chain Dynamics
Global furniture production and availability are significantly influenced by the intricate web of supply chains. Fluctuations in material sourcing, manufacturing processes, and transportation networks create ripples throughout the industry. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for manufacturers to adapt and remain competitive in the face of global challenges.The global furniture industry relies heavily on intricate supply chains spanning multiple countries.
These chains are vulnerable to disruptions from various factors, including geopolitical instability, natural disasters, and pandemic-related lockdowns. These disruptions can cause delays in material delivery, production bottlenecks, and ultimately, shortages in the availability of finished furniture products.
Impact of Global Supply Chain Disruptions
Supply chain disruptions have a profound impact on furniture production and availability. Disruptions in raw material supply, particularly for wood, metal, and fabric, can halt production lines. Delays in the delivery of components, like hinges or drawer systems, can cause significant production delays. These disruptions often result in increased lead times for furniture orders, potentially impacting customer satisfaction and sales figures.
For example, the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic caused significant disruptions in the global supply chain, leading to shortages of critical components and a rise in furniture prices.
Role of Logistics and Transportation
Efficient logistics and transportation play a pivotal role in fulfilling global furniture demand. The transportation of bulky furniture across vast distances requires specialized logistics solutions. Sea freight, air freight, and trucking all have varying costs and delivery times, impacting the final price and availability of furniture in different markets. Effective route planning, optimized warehousing, and real-time tracking systems are essential for timely delivery.
The complexity of shipping furniture globally necessitates partnerships with specialized logistics providers.
Strategies to Mitigate Supply Chain Risks
Furniture manufacturers employ various strategies to mitigate supply chain risks. Diversifying sourcing locations for raw materials is a common approach to reduce reliance on single suppliers. This allows for backup plans in case of disruptions in one region. Building stronger relationships with reliable suppliers and establishing alternative manufacturing partners are also crucial. Furthermore, implementing robust inventory management systems and forecasting demand accurately can help anticipate potential shortages and maintain sufficient stock levels.
Investing in advanced technology, like predictive analytics, allows manufacturers to anticipate and respond proactively to potential disruptions.
Different Supply Chain Models
Furniture companies employ a variety of supply chain models, ranging from vertically integrated structures to more decentralized ones. Vertical integration, where a company controls multiple stages of the supply chain, allows for tighter control and potentially lower costs. However, it also exposes the company to greater risk if a single point in the chain is disrupted. Conversely, decentralized models, which rely on external suppliers and manufacturers, offer greater flexibility but potentially increase complexity and coordination challenges.
The choice of model depends on factors such as company size, production scale, and market conditions.
Critical Factors Impacting Furniture Manufacturing Costs
Several factors significantly influence the cost of furniture manufacturing. The cost of raw materials, including wood, metal, and fabrics, plays a critical role. Labor costs, particularly in manufacturing hubs, are another significant expense. Transportation costs and logistics fees add to the total production expenses. Manufacturing processes, including assembly methods and the use of specialized equipment, also influence the cost.
The cost of design and prototyping stages, and the level of customization, further influence the overall cost.
Comparative Cost Analysis of Furniture Manufacturing
| Material | Manufacturing Process | Estimated Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solid Wood | Traditional Carpentry | $150-$500 | High quality, craftsmanship, potentially higher labor costs |
| MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard) | Automated Assembly | $50-$250 | Faster production, potentially lower quality |
| Laminate | Automated Assembly | $30-$150 | Low cost, mass production |
| Recycled Materials | Sustainable Manufacturing | $100-$400 | Environmentally friendly, potentially higher costs initially |
Note: Costs are estimates and vary based on specific design, volume, and market conditions.
Consumer Behavior and Preferences
Source: slideserve.com
Consumer behavior significantly influences furniture demand, dictating styles, types, and purchase decisions. Modern consumers are actively seeking furniture that reflects their personal values, lifestyle, and aesthetic preferences. This evolving landscape is driving innovation in the furniture industry, demanding adaptability and a keen understanding of current trends.
Consumer Preferences Shaping Furniture Demand
Consumer preferences are a key driver in the furniture industry, influencing the demand for specific styles and types. A growing emphasis on sustainability and eco-friendly materials is evident, with consumers increasingly favoring furniture made from recycled or reclaimed wood, bamboo, or other sustainable sources. Furthermore, a focus on functionality and versatility is prominent, with modular and multi-functional furniture pieces gaining popularity.
The desire for durable and long-lasting furniture, while considering affordability, also plays a pivotal role in consumer choices.
Influence of Social Media and Online Platforms
Social media and online platforms have become powerful tools in shaping furniture purchasing decisions. Visual platforms like Instagram and Pinterest provide inspiration and showcase diverse styles, influencing consumer choices. Online retailers offer extensive product catalogs, enabling consumers to compare prices and features, further impacting their buying habits. Reviews and recommendations from other consumers significantly influence decisions, making online presence crucial for furniture brands.
Customization and Personalization
Customization and personalization are vital aspects of meeting consumer demand. Consumers desire furniture that complements their unique style and living spaces. The rise of online configurators allows consumers to personalize furniture, choosing fabrics, finishes, and dimensions to precisely meet their needs. This level of personalization empowers consumers and enhances their satisfaction. This tailoring to individual tastes is a defining factor in the furniture market.
Adapting to Evolving Consumer Preferences
Furniture companies are actively adapting to evolving consumer preferences. Companies are integrating sustainable materials and production methods into their operations, responding to environmentally conscious consumers. They are offering a wider range of sizes, colors, and finishes to cater to a diverse clientele. Furniture companies are also emphasizing functionality and versatility, providing pieces that serve multiple purposes, such as storage and seating.
Furniture Rental and Subscription Services
The growth of furniture rental and subscription services is fueled by several factors. Consumers are seeking flexibility and affordability, often opting for rental options to try different styles or avoid large upfront costs. These services address the needs of individuals who want to refresh their home décor without committing to a long-term purchase. Rental models offer convenience and reduce the burden of owning and maintaining furniture.
Top 5 Furniture Styles Favored by Consumers
| Region | Style 1 | Style 2 | Style 3 | Style 4 | Style 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| North America | Modern Farmhouse | Mid-Century Modern | Scandinavian | Industrial | Bohemian |
| Europe | Scandinavian | Minimalist | Industrial | Modern | Vintage |
| Asia | Contemporary | Traditional | Minimalist | Modern | Japanese |
| South America | Bohemian | Modern | Colonial | Rustic | Traditional |
Note: This table provides a general overview and may not reflect all regional preferences. Specific preferences can vary significantly within regions and are subject to change.
Emerging Technologies and Materials

Source: chapv.com
Advanced materials and digital technologies are rapidly reshaping the furniture industry, driving innovation and creating new possibilities for design and production. These advancements are not just about aesthetics; they are fundamentally altering how furniture is conceived, manufactured, and ultimately interacts with the environment. The implications extend from improved sustainability to entirely new ways of creating furniture.
Advanced Materials in Furniture Manufacturing
The use of advanced materials in furniture manufacturing is no longer a futuristic concept. Manufacturers are increasingly incorporating composites, polymers, and high-performance metals into their designs. These materials offer enhanced durability, reduced weight, and improved aesthetic options, opening new avenues for creative expression. For instance, carbon fiber reinforced polymers are becoming increasingly popular for high-end furniture, delivering both strength and lightness.
3D Printing and Digital Technologies in Furniture Design and Production
D printing is transforming furniture design and production by enabling the creation of complex geometries and personalized designs. It allows for intricate details and customized solutions that were previously impossible. Additive manufacturing, such as 3D printing, also facilitates prototyping and rapid iteration, reducing the time and cost of bringing new furniture designs to market. Furthermore, digital tools empower designers to visualize and manipulate designs in virtual environments before physical production, leading to more efficient and effective design processes.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Furniture Design and Manufacturing
AI and machine learning are beginning to play a crucial role in optimizing furniture design and manufacturing processes. AI algorithms can analyze vast datasets to identify trends in consumer preferences, predict material performance, and optimize manufacturing workflows. For example, AI-powered design tools can suggest materials and configurations to meet specific criteria, like strength, weight, or aesthetic appeal, streamlining the design process.
Environmental Impact of New Materials in Furniture
The environmental impact of new materials is a critical consideration in furniture production. While some advanced materials offer improved durability and reduced weight, others might have significant environmental footprints during their production. Careful consideration of the lifecycle of the material, from extraction to disposal, is essential to minimize the overall environmental impact. Sustainable sourcing practices and material selection are vital for mitigating the negative effects on ecosystems.
Emerging Materials in Furniture Manufacturing
| Material | Properties | Applications | Environmental Impact Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recycled Plastic Composites | Durable, lightweight, cost-effective, readily available | Chairs, tables, storage units, outdoor furniture | Reduced reliance on virgin materials, lower carbon footprint, but recycling processes and potential microplastic concerns need careful management. |
| Bamboo | Strong, renewable, fast-growing, lightweight | Flooring, furniture frames, panels, tableware | Sustainable alternative to wood, but careful consideration of water usage during cultivation and transportation is required. |
| Bio-based Polymers | Renewable, biodegradable, potentially compostable | Chair cushions, upholstery fabrics, packaging materials | Lower carbon footprint compared to petroleum-based plastics, but potential for variable performance and cost compared to traditional plastics. |
| Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymers (CFRP) | High strength-to-weight ratio, lightweight, durable | High-end furniture, sports equipment, aerospace components | High energy consumption in manufacturing process, reliance on carbon fiber production from fossil fuels. Recycling and disposal are important considerations. |
| Advanced Wood Composites | Stronger than solid wood, lower cost, reduced weight | Furniture frames, panels, decorative elements | Minimizing formaldehyde emissions, ensuring sustainable sourcing of wood fibers, and proper disposal to avoid harmful waste. |
Bio-based Materials for Sustainable Furniture Production
Bio-based materials offer a promising avenue for sustainable furniture production. These materials, derived from renewable sources like plants and agricultural waste, can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of furniture. The potential of mycelium, a network of fungal filaments, is also being explored for its strength, unique aesthetics, and potential for rapid growth. The use of these materials can contribute to a more circular economy for furniture manufacturing.
Case Studies of Furniture Innovation: Global Demand Driving Furniture Innovation
Global demand for furniture is constantly evolving, prompting innovative solutions across design, production, and sustainability. Companies that effectively adapt to these trends often experience significant success. This section examines various case studies highlighting successful adaptations, strategies for sustainability, the influence of design trends, and the application of emerging technologies in the furniture industry.
A Successful Furniture Company Adapting to Global Demand
IKEA, a global furniture retailer, has demonstrated a remarkable ability to adapt to diverse global markets. Their strategy centers on low-cost, standardized designs, which allow for efficient production and distribution worldwide. Furthermore, they offer a wide range of styles and price points, catering to a vast consumer base. IKEA’s emphasis on modular furniture enables customers to customize their spaces, fostering a sense of personalization.
This adaptability, combined with their strong supply chain management, has made them a global leader in the furniture market.
Strategies Employed by a Furniture Manufacturer in Addressing Sustainability Challenges
Many furniture manufacturers are implementing strategies to reduce their environmental impact. One approach involves utilizing recycled or sustainable materials, such as bamboo or reclaimed wood. Another strategy focuses on minimizing waste throughout the production process. This can include optimizing material use, implementing closed-loop systems, and using energy-efficient manufacturing technologies. Furthermore, some manufacturers are embracing circular economy models, which aim to extend the lifespan of furniture through repair, reuse, and recycling programs.
These initiatives not only enhance the company’s image but also contribute to a more sustainable future.
The Role of Design Trends in Driving Sales
Design trends significantly impact furniture sales. For instance, the rise of Scandinavian design principles, characterized by minimalism and natural materials, has led to increased demand for simple, functional furniture. Likewise, the growing interest in sustainable and eco-friendly products has fueled the adoption of materials like bamboo and reclaimed wood. Companies that stay abreast of these evolving preferences and integrate them into their product lines tend to perform better in the market.
Companies that successfully anticipate and adapt to shifting design preferences can see a substantial boost in sales.
Utilizing Emerging Technologies in Furniture Production
Emerging technologies are transforming furniture production. 3D printing is enabling the creation of intricate and customized designs, reducing manufacturing time and costs. Additionally, the use of advanced materials like carbon fiber and composite woods can enhance the durability and aesthetic appeal of furniture. Furthermore, digital design tools are allowing for more precise and efficient manufacturing processes. This shift towards technology-driven approaches often leads to higher-quality products and improved production efficiency.
Summary Table of Case Studies
| Company | Innovation Focus | Strategies Employed | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| IKEA | Adaptability to global markets, modular designs, and low-cost production | Standardized designs, efficient supply chains, and wide range of price points | Global market leader, strong consumer base, and high sales volume |
| Herman Miller | Sustainable materials and manufacturing practices | Use of recycled materials, minimizing waste, and circular economy models | Strong brand image, commitment to sustainability, and positive environmental impact |
| Knoll | Integrating design trends into product lines | Keeping abreast of design trends, incorporating them into new designs, and offering innovative aesthetics | Increased sales and market share, meeting consumer demand, and strong brand recognition |
Ultimate Conclusion
In conclusion, the global furniture market is undergoing a significant evolution, driven by consumer demand for innovative and sustainable products. The integration of technology, the importance of sustainability, and the complexities of global supply chains are all major factors shaping this transformation. This evolution promises exciting new opportunities for businesses and consumers alike.
Quick FAQs
What are the key economic factors influencing global furniture demand?
Factors like economic growth, disposable income, and consumer confidence directly impact the demand for furniture. Increased disposable income often leads to higher spending on home furnishings, while economic downturns can lead to decreased demand. Global economic trends, like inflation and interest rates, also play a crucial role.
How are supply chain disruptions affecting furniture production?
Global supply chain disruptions, such as those caused by pandemics or geopolitical events, can significantly impact furniture production and availability. Disruptions in raw material sourcing, manufacturing, and logistics can lead to delays, price increases, and shortages.
What role does customization play in meeting consumer demands?
Consumers increasingly seek personalized and customized furniture options. This is reflected in the rise of online furniture retailers offering greater choice and customization capabilities. Companies are responding to this trend by offering more design flexibility and allowing consumers to tailor products to their specific needs.
How are emerging technologies transforming furniture design?
Emerging technologies like 3D printing and AI are significantly altering furniture design and manufacturing processes. These technologies allow for greater design flexibility, faster prototyping, and potentially more sustainable manufacturing methods.