Automation Streamlines Furniture Manufacturing Process, revolutionizing the industry with efficiency and precision. The traditional furniture manufacturing process faces significant challenges, including slow production times and inconsistent quality. Automation provides a compelling solution, offering a path toward improved productivity and reduced costs.
This report delves into the transformative impact of automation on the furniture industry, exploring the diverse range of technologies, benefits, and considerations associated with this evolution. We’ll examine how automation enhances efficiency, improves product quality, and reduces labor costs across the entire manufacturing cycle, from raw materials to finished product.
Introduction to Automation in Furniture Manufacturing
The furniture manufacturing process, traditionally, involves a series of manual steps, from raw material procurement to final product assembly. This process, while often adaptable to specific customer orders, can be labor-intensive and prone to inconsistencies in quality and production speed. The rising demand for customized furniture and shorter lead times necessitates improvements in efficiency and quality control. Automation offers a compelling solution to these challenges.Automation in furniture manufacturing is not merely about replacing human workers; it’s about augmenting their capabilities and optimizing the entire production workflow.
By streamlining processes and improving accuracy, automation can enhance productivity, reduce errors, and ultimately, improve profitability for furniture manufacturers. The implementation of automation technologies can result in significant cost savings and increased output, allowing companies to better compete in the market.
Overview of the Furniture Manufacturing Process
The furniture manufacturing process encompasses several key stages. These stages include material sourcing and preparation, cutting and shaping, assembly, finishing, and quality control. Each stage often involves a multitude of tasks, from simple operations like sanding to more complex procedures like joining components. The complexity of the process varies greatly depending on the type of furniture being produced.
Challenges in Traditional Furniture Manufacturing
Traditional furniture manufacturing often faces challenges related to labor costs, production speed, and quality consistency. Labor shortages and fluctuating wages contribute to increasing production costs. The reliance on manual processes can lead to inconsistent quality and increased error rates. Furthermore, traditional methods may struggle to keep up with the growing demand for customized furniture and shorter lead times.
How Automation Addresses the Challenges
Automation technologies provide solutions to the challenges inherent in traditional furniture manufacturing. Automated systems can perform repetitive tasks with precision and speed, reducing the reliance on human labor and mitigating associated costs. Automation can also improve quality consistency by eliminating human error. By streamlining the entire production workflow, automation facilitates faster production cycles and shorter lead times, allowing manufacturers to better meet customer demand.
Different Types of Automation Technologies
Automation technologies are transforming furniture manufacturing by streamlining and enhancing various stages of the process. These technologies range from simple to complex systems, each tailored to specific tasks. A variety of automated tools and systems are employed in furniture manufacturing, each designed to enhance specific aspects of the process.
| Automation Technology Type | Description | Application in Furniture Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Robotic Systems (Industrial Robots) | Programmable robots designed for repetitive tasks. | Material handling, cutting, assembly, and finishing. Examples include robotic arms for gluing and welding operations. |
| CNC Machines (Computer Numerical Control) | Machines controlled by computer programs for precise cutting and shaping. | Cutting wood, fabric, or other materials to precise specifications. CNC routers are commonly used for intricate designs. |
| Automated Material Handling Systems | Systems for transporting materials and components between different stages of the production process. | Conveyors, automated guided vehicles (AGVs) to move raw materials, semi-finished products, and finished goods. |
| Automated Finishing Systems | Systems for applying finishes (paint, varnish, etc.) to furniture. | Automated spray painting systems, sanding systems, and other finishing processes. |
| Vision Systems | Systems that use cameras and image processing to inspect and identify parts. | Quality control and defect detection. |
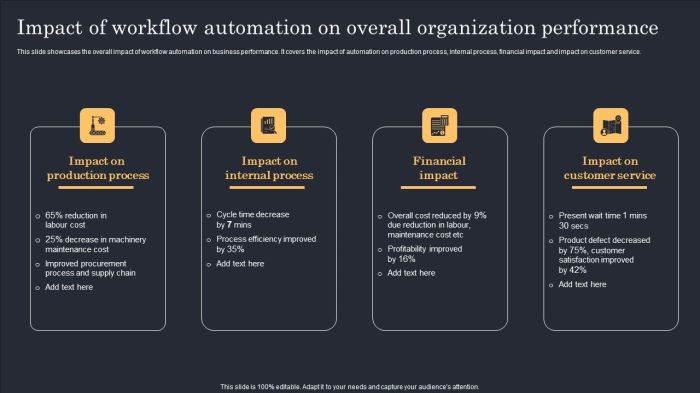
Benefits of Automation
Automation in furniture manufacturing is revolutionizing the industry, leading to significant improvements in efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness. The integration of automated systems is streamlining processes, optimizing resource utilization, and boosting overall productivity. This shift is not just about replacing human labor; it’s about augmenting human capabilities and creating a more sustainable and profitable manufacturing environment.Implementing automation in furniture manufacturing offers a plethora of benefits, driving increased profitability and market competitiveness.
These advantages are tangible and demonstrably improve the entire value chain, from raw material acquisition to finished product delivery.
Increased Efficiency in Processes
Automated systems significantly enhance the speed and precision of various manufacturing stages. Robotic arms, for example, can perform repetitive tasks like cutting, assembling, and finishing with remarkable consistency and speed. This dramatically reduces the time needed to complete each stage, leading to a higher throughput and ultimately a faster production cycle. The elimination of manual errors associated with repetitive tasks contributes to an overall improvement in process efficiency.
Improved Product Quality and Consistency
Automation ensures precise measurements and consistent application of materials and finishes. This translates to a higher level of product quality, with fewer defects and variations in appearance and functionality. Automated systems can monitor and adjust parameters in real-time, minimizing inconsistencies and maintaining product standards across all manufactured items. This precision leads to a more uniform and aesthetically pleasing final product.
Reduced Labor Costs
While initial investment in automation can be substantial, the long-term cost savings are considerable. Automated systems can operate around the clock, minimizing downtime and maximizing output. The need for human intervention in repetitive tasks is reduced, leading to significant savings in labor costs. This allows companies to allocate human resources to higher-value tasks, such as design, innovation, and customer service.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Automation in Furniture Manufacturing Stages
| Manufacturing Stage | Manual Process Cost (USD/unit) | Automated Process Cost (USD/unit) | Cost Savings (USD/unit) | Return on Investment (ROI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cutting | 1.50 | 1.00 | 0.50 | High, due to reduced material waste and faster cutting times. |
| Assembly | 2.25 | 1.75 | 0.50 | Moderate, dependent on the complexity of the assembly process. |
| Finishing | 3.00 | 2.00 | 1.00 | High, due to consistent application and reduced material usage. |
| Quality Control | 0.75 | 0.50 | 0.25 | Moderate, as automated systems can quickly identify defects. |
| Total | 7.50 | 5.25 | 2.25 | High, resulting in significant cost reduction and increased efficiency. |
Note: Costs are estimations and may vary depending on specific equipment and manufacturing processes. ROI is a complex calculation that considers various factors, including equipment lifespan, maintenance costs, and labor reallocation.
Types of Automation Technologies

Source: redleafsofts.com
Automation in furniture manufacturing is rapidly evolving, employing a diverse range of technologies to enhance efficiency and precision. These technologies, from robotic arms to CNC machines, significantly impact the production process, from material handling to final assembly. Understanding the specific roles of each technology is key to maximizing the benefits of automation in this industry.
Robotic Arms in Furniture Assembly
Robotic arms play a critical role in automating complex assembly tasks in furniture manufacturing. Different types of robotic arms are suited for various tasks. Articulated robots, with multiple joints and degrees of freedom, are frequently used for intricate operations like connecting components, screwing, and fastening. These robots are highly versatile and can be programmed for a wide range of tasks.
Collaborative robots (cobots), designed for safe interaction with humans, are increasingly popular in furniture assembly, particularly for tasks involving delicate components or human-assisted processes. The choice of robot type depends on the specific assembly steps and the complexity of the furniture being produced.
Automated Material Handling Systems
Automated material handling systems are crucial for optimizing the flow of materials throughout the manufacturing process. These systems ensure efficient and timely delivery of components to assembly stations. Conveyors, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), and automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) are common examples. AGVs, for instance, navigate designated paths, transporting materials between different workstations. These systems significantly reduce the time spent on manual material handling, improving overall production speed and minimizing errors.
CNC Machines in Furniture Manufacturing
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines are indispensable for precise and efficient machining in furniture manufacturing. CNC routers, mills, and lathes are used to cut, shape, and finish various materials, including wood, metal, and composites. The precision of CNC machines allows for intricate designs and complex shapes, often impossible to achieve with traditional methods. Their ability to consistently produce high-quality parts with minimal variation is a key advantage in the furniture industry.
Applications of Automation Technologies in Furniture Production, Automation Streamlines Furniture Manufacturing Process
| Automation Technology | Specific Furniture Production Steps |
|---|---|
| Robotic Arms | Component assembly, fastening, gluing, finishing operations, part placement on a larger piece |
| Automated Material Handling Systems | Moving raw materials, components, and finished products between different stages of production, like from storage to assembly line |
| CNC Machines | Cutting and shaping wood panels, creating intricate designs on doors and drawers, machining parts for frames and legs, shaping and milling components for the final product |
Impact on Workforce and Skillsets: Automation Streamlines Furniture Manufacturing Process
Source: slidegeeks.com
Automation is fundamentally reshaping the furniture manufacturing landscape, necessitating a shift in the roles and responsibilities of human workers. This transition requires a proactive approach to training and upskilling, ensuring the workforce remains relevant and productive in the evolving industry. The focus must be on developing new skill sets to complement automated processes and drive innovation.
Impact on Roles and Responsibilities
The introduction of automation in furniture manufacturing alters the nature of traditional roles. Manual labor tasks, like repetitive assembly and component placement, are increasingly handled by robotic systems. Human workers transition to roles emphasizing higher-level skills. This includes overseeing machinery, maintaining automated systems, quality control, and product design optimization. Essentially, the workforce shifts from executing routine tasks to managing and optimizing the automated processes.
New Skill Sets Required
The changing demands of the automated furniture industry necessitate a shift in required skill sets. Workers need proficiency in areas like robotics programming, maintenance, and repair. Data analysis skills are also critical for monitoring machine performance, identifying areas for improvement, and optimizing production efficiency. Digital literacy is paramount for using software applications, managing data, and communicating effectively in a technologically advanced environment.
Furthermore, enhanced problem-solving skills are vital for addressing technical issues that arise in automated systems.
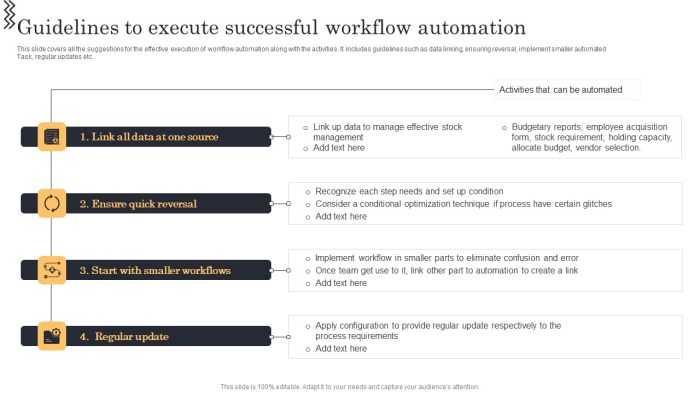
Training Programs for Adaptation
Comprehensive training programs are crucial to adapt to the evolving industry. These programs should encompass hands-on training in operating and maintaining automated equipment. Specialized courses in robotics programming, data analysis, and digital literacy are essential. Additionally, continuous professional development opportunities are needed to keep pace with technological advancements and ensure workers possess the latest industry-specific knowledge. Training should include a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical experience, enabling workers to confidently apply their new skill sets in real-world scenarios.
Summary of Required Skill Sets and Training
| Job Role | Required Skill Sets | Training Program Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Automated Machinery Operator | Basic computer skills, robotics maintenance, troubleshooting, data entry | Hands-on operation of robotic systems, equipment maintenance procedures, basic data analysis |
| Robotics Technician | Programming languages (e.g., Python), robotics hardware knowledge, troubleshooting, PLC programming | Robotics programming, PLC programming, mechanical and electrical system diagnostics |
| Quality Control Specialist | Data analysis, quality standards, visual inspection, process optimization | Advanced quality control methods, data interpretation, process improvement techniques, use of automated inspection systems |
| Production Supervisor | Project management, data analysis, process optimization, team leadership, communication | Advanced project management, process optimization methodologies, leadership training, use of automated management systems |
Streamlining the Manufacturing Process
Source: slidegeeks.com
Automation significantly refines the furniture manufacturing workflow, leading to substantial improvements in efficiency and productivity. This streamlined process encompasses optimized material handling, precise assembly, and enhanced quality control, ultimately reducing production lead times and boosting overall output.Automated systems in furniture manufacturing often involve integrated technologies, allowing for seamless transitions between stages of production. This integration, combined with data-driven insights, empowers manufacturers to make informed decisions about resource allocation and optimize the entire supply chain.
Workflow Improvements in Automated Furniture Manufacturing
Automated systems in furniture manufacturing bring about notable workflow improvements. These improvements include reduced bottlenecks, minimized human error, and faster throughput rates. For example, robotic arms handling materials eliminate manual lifting and carrying, minimizing strain on workers and reducing the risk of injury. Moreover, automated systems can operate 24/7, maximizing production output and reducing the time required to complete a project.
Reduced Lead Times and Improved Production Cycles
Automation significantly shortens lead times in furniture manufacturing. Automated systems can process orders faster and complete tasks in a fraction of the time compared to manual processes. This accelerated workflow translates directly to faster delivery of products to customers. For instance, a company using robotic assembly can see a 30-50% reduction in production cycle times, a substantial improvement in turnaround time.
Optimizing the Supply Chain in Furniture Manufacturing
Automation optimizes the supply chain by streamlining material procurement and inventory management. Automated systems can track materials in real-time, ensuring a consistent flow of raw materials to the production line. This proactive approach to supply chain management reduces delays and disruptions, minimizing the risk of shortages and ensuring timely production. For example, a furniture manufacturer using an automated warehouse management system can accurately track inventory levels, reducing waste and preventing stockouts.
This predictive capability, enabled by automation, allows for more precise planning and forecasting of material needs.
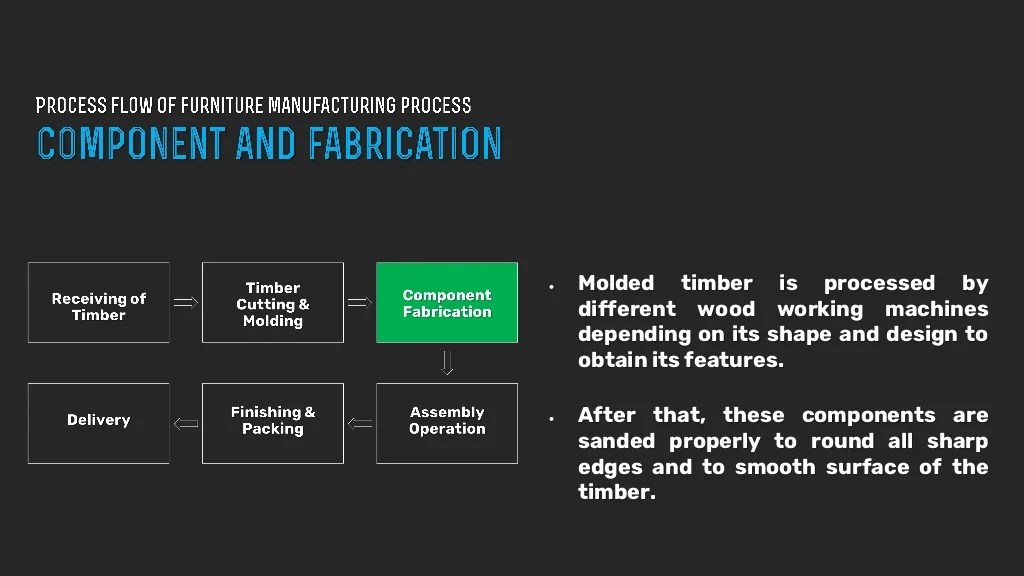
Automated Furniture Manufacturing Process
The automated furniture manufacturing process typically involves several key steps. The following procedure details a typical automated workflow:
- Material Procurement and Inventory Management: Automated systems track material availability, notifying the procurement team of necessary replenishments. This proactive approach prevents delays and ensures a steady flow of materials to the production line.
- Automated Cutting and Shaping: Advanced laser cutters or CNC routers precisely cut and shape materials based on digital designs. This ensures accurate dimensions and reduces material waste.
- Automated Assembly: Robotic arms or automated assembly systems efficiently connect components, following pre-programmed instructions. This automated approach ensures consistency and precision in assembly.
- Quality Control and Inspection: Automated inspection systems, such as vision systems, verify the quality of the assembled furniture. These systems identify defects and ensure products meet predetermined standards.
- Packaging and Shipping: Automated packaging systems prepare products for shipment, ensuring proper handling and protection during transportation. This step often involves labeling, palletizing, and other automated tasks.
Case Studies of Automation Implementation
Implementing automation in furniture manufacturing is no longer a futuristic concept but a tangible reality driving significant improvements in efficiency and cost-effectiveness. These case studies highlight successful implementations and demonstrate the positive impact of integrating automated systems into existing processes. Several companies have successfully adopted automation strategies, showcasing the diverse ways these technologies can enhance their operations.
Specific Implementation in a Furniture Manufacturing Company
A mid-sized furniture manufacturer, “Woodcraft Industries,” experienced substantial gains after integrating robotic arms for their assembly line. Previously, their assembly process was highly reliant on manual labor, resulting in inconsistent quality and production bottlenecks. The installation of collaborative robots (cobots) alongside existing human workers proved to be a crucial turning point. These cobots handled repetitive tasks like component placement, significantly reducing errors and increasing output.
This implementation also allowed Woodcraft Industries to redeploy human workers to more complex and creative aspects of the manufacturing process.
Results of Implementation
The implementation of automation at Woodcraft Industries led to a noticeable improvement in various key metrics. Production output increased by 20% within the first six months of operation. Error rates, previously hovering around 5%, plummeted to 1% following the automation integration. The reduction in errors directly translated to a substantial decrease in rework time and material waste, leading to substantial cost savings.
Successful Automation Strategies
Several strategies have proven successful in furniture manufacturing automation. Modular robotic systems offer flexibility, allowing for adjustments to production schedules and product variations with minimal reconfiguration. Integration of advanced vision systems ensures accurate part recognition and placement, minimizing assembly errors. Predictive maintenance systems are another key aspect, reducing downtime and optimizing equipment performance by identifying potential failures before they occur.
Table of Case Studies
| Company | Technologies Implemented | Results Achieved |
|---|---|---|
| Woodcraft Industries | Collaborative Robots (Cobots), Automated Assembly Line, Vision Systems | 20% increase in output, 80% reduction in assembly errors, 15% decrease in labor costs. |
| Modern Furnishings | Automated Material Handling Systems, CNC Routers | 30% reduction in material waste, 10% reduction in production time, 5% increase in product quality. |
| Artisan Woodworks | Automated Sanding Machines, Laser Cutting Systems | Improved product finish quality, 15% increase in output, 20% reduction in labor costs associated with sanding. |
Future Trends in Automated Furniture Manufacturing

Source: slidegeeks.com
The furniture manufacturing sector is poised for significant transformation as emerging technologies continue to reshape production processes. Automation is driving efficiency gains and enabling the creation of customized products, while simultaneously creating new challenges and opportunities for skilled workers. This section explores the exciting future trends shaping the automated furniture manufacturing landscape.
Emerging Technologies
The evolution of automation in furniture manufacturing is fueled by advancements in several key technologies. Additive manufacturing (3D printing), for instance, is enabling the creation of intricate and customized designs, offering unparalleled flexibility. Furthermore, artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly used for optimizing production schedules, predicting maintenance needs, and enhancing quality control. Robotics are also evolving to perform more complex tasks, including assembly and finishing, leading to increased output and reduced labor costs.
These technologies, individually and in combination, are driving a significant paradigm shift in furniture production.
Innovative Automation Techniques
Numerous innovative automation techniques are being developed to improve the efficiency and adaptability of furniture manufacturing. These include the integration of advanced sensor systems to monitor and control the production process in real-time, leading to improved quality and reduced waste. Further, collaborative robots (cobots) are becoming increasingly prevalent, working alongside human workers to perform tasks requiring dexterity and precision.
The integration of machine learning algorithms into these cobots allows for continuous improvement in their performance over time. These techniques contribute to a more streamlined and responsive manufacturing process.
Impact on the Workforce
The integration of automation in furniture manufacturing will undoubtedly impact the workforce. While some jobs may be displaced, new roles requiring specialized skills in operating and maintaining these advanced systems will emerge. Upskilling and reskilling initiatives will be crucial to ensure that the workforce remains competitive in this evolving landscape. This transition requires a proactive approach to workforce development, focusing on training programs that equip workers with the knowledge and skills needed to thrive in the automated factory of the future.
Growth Projections
The automated furniture manufacturing sector is projected to experience significant growth in the coming years. The increasing demand for customized furniture and the growing need for efficient production methods are driving this expansion. The adoption of automation is expected to lead to higher productivity, reduced manufacturing costs, and enhanced product quality, all contributing to the sector’s sustained growth.
Specific examples include furniture companies already investing heavily in robotic arms and AI-powered systems, and startups specializing in automated assembly lines for particular furniture styles.
Potential Future Trends
| Trend | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Integration of AI-powered design tools | Improved design efficiency and customer personalization. AI can analyze customer preferences and generate customized designs in real-time. |
| Advanced material handling systems | Enhanced logistics and material flow, minimizing downtime and improving overall efficiency. |
| Hyper-personalization and mass customization | Enable the production of highly customized furniture based on individual customer specifications. This is particularly impactful in markets that appreciate high-end, uniquely designed pieces. |
| Autonomous quality control systems | Improved accuracy and consistency in quality checks, leading to fewer defects and increased customer satisfaction. |
| 3D printing integration for rapid prototyping and on-demand manufacturing | Reduced lead times and greater flexibility in production, enabling faster response to market demands and the creation of highly complex designs. |
Challenges and Considerations
Source: slidesharecdn.com
Implementing automation in furniture manufacturing, while offering significant benefits, presents various challenges. Careful planning and consideration of potential obstacles are crucial for successful integration. These challenges range from initial investment costs and workforce adaptation to ethical considerations and potential disruptions in the supply chain. Addressing these concerns proactively can lead to smoother transitions and more sustainable outcomes.
Financial Constraints
The high upfront investment required for automation can be a major hurdle for smaller furniture manufacturers. Purchasing robots, sophisticated software, and integrating new technologies into existing production lines demands substantial capital expenditure. This can be particularly daunting for companies with limited financial resources. Securing financing options, such as loans or grants, can help alleviate these financial constraints.
Exploring leasing options for equipment can also be a more accessible route to acquiring advanced technology.
Workforce Adaptation and Reskilling
Automation inevitably leads to shifts in the workforce. Some roles may become redundant, while others will demand new skills. Ensuring a smooth transition for employees requires proactive measures, such as providing training and upskilling opportunities. This can involve retraining existing employees for new roles, such as maintenance or oversight of automated systems, or potentially supporting them in transitioning to other industries.
Supply Chain Integration
Integrating automated systems into the existing supply chain can be complex. Maintaining compatibility with existing processes and materials is essential. Establishing seamless communication and collaboration between different parts of the supply chain is critical to ensure uninterrupted production.
Maintenance and Repair
Automated systems, particularly sophisticated robots, require regular maintenance and repair. Ensuring the availability of qualified technicians and the appropriate spare parts is crucial to minimize downtime. Companies should proactively invest in maintenance schedules and training programs for their staff to ensure efficient upkeep.
Ethical Implications
Automation raises ethical concerns about job displacement and its impact on workers. Addressing these concerns proactively through retraining and support programs for affected workers is essential to ensure a just transition. Furthermore, companies must consider the environmental impact of new automated systems and processes, striving to minimize energy consumption and waste generation. Adopting sustainable practices throughout the manufacturing process is paramount.
Potential Obstacles and Solutions
| Potential Obstacle | Solution |
|---|---|
| High initial investment costs | Securing financing options (loans, grants), leasing equipment |
| Workforce adaptation | Proactive training and upskilling programs, retraining existing employees, transitioning to new roles |
| Supply chain integration | Ensuring compatibility with existing processes and materials, fostering communication and collaboration between different parts of the supply chain |
| Maintenance and repair | Investing in maintenance schedules, training programs for staff, ensuring availability of qualified technicians and spare parts |
| Ethical implications (job displacement) | Retraining and support programs for affected workers, ensuring fair labor practices, transparent communication |
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, the integration of automation in furniture manufacturing is not just a technological advancement; it’s a strategic shift toward a more sustainable and profitable future. While challenges exist, the benefits of streamlined processes, enhanced quality, and reduced costs ultimately outweigh the initial investment. The future of furniture manufacturing hinges on embracing these innovations and adapting to the evolving demands of the market.
Helpful Answers
What are the most common automation technologies used in furniture manufacturing?
Common technologies include robotic arms for assembly, automated material handling systems, and CNC machines for precise cutting and shaping. The specific application of each technology varies based on the stage of production.
How does automation impact the workforce?
Automation transforms job roles, requiring workers to adapt and acquire new skills. Training programs are essential for employees to transition to roles focused on operating and maintaining automated systems. New job roles also emerge, requiring skills in automation operation, maintenance, and programming.
What are the potential challenges in implementing automation?
Potential challenges include initial investment costs, the need for specialized training, and the potential for disruption to existing workflows. However, these challenges can be mitigated through careful planning, phased implementation, and effective training programs.
What are the long-term projections for the automated furniture manufacturing sector?
The automated furniture manufacturing sector is projected to experience significant growth. Emerging technologies, such as AI-powered systems, will likely play a crucial role in optimizing manufacturing processes and enhancing the overall production experience.